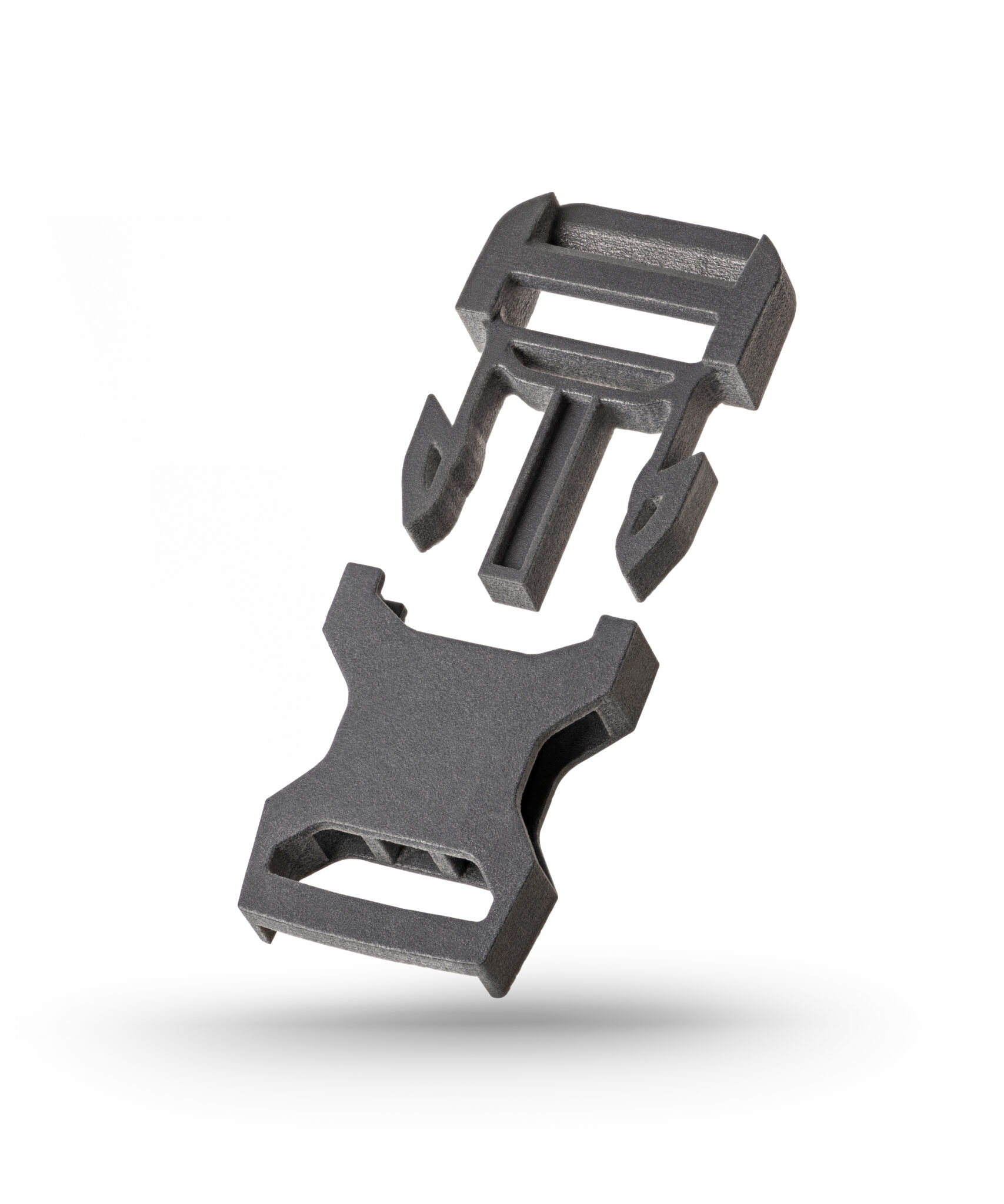
High-Volume Production vs. Low-Volume Production
Let’s explore the key principles of high-volume production and discuss all the numbers, pros, and cons behind it.
What Is High-Volume Production?
In essence, high-volume production is the ability to mass-produce products or parts quickly and efficiently.
Low-Volume Production
- 1-10,000 parts per year
- Short lead times and low setup costs
Mid-Volume Production
- Less than 10,000 or 50,000 parts per year
- Moderate lead times and setup costs
High-Volume Production
- Greater than 50,000 parts per year
- Moderate lead times and setup costs
Difference Between High-Volume and Low-Volume Production
Context is important when defining what is considered to be low-volume or high-volume production. It boils down to the fact that different manufacturing processes are more cost-effective at a certain level of production than others.
Other important factors that impact production cost at volume are:
- Setup time
- Adaptability to implement design changes
- Precision and accuracy of producing the part at volume
High-Volume Production
High-volume production is ideal for products that are in high demand, such as commodities. Companies trying to make a prototype or product and quickly mass-produce it to meet market demand will find the most use (and resource savings) from manufacturing in high volumes.
Unit costs are significantly less expensive than low-volume production unit costs. For example, you may be looking at $700 per unit for low-volume, but only $0.02 per unit for high-volume.
Pros
- Quick turnaround time
- Ideal for large orders
- Manufacturers can meet more of market demand
- Greater ROI due to saving on production costs
Cons
- Inflexibility with things like design changes
- Limited production capacity
- Not ideal for small orders
- Require a large amount of resources with traditional manufacturing
Low-Volume Production
Low-volume production is excellent for small businesses or businesses that are introducing a new product slowly into the market. This production volume is generally used for prototypes and custom or limited-edition products.
Pros
- Lower minimum order quantities
- Lower overhead costs
- Less material waste
- Greater flexibility with iterative changes
- Fast prototyping of different designs
Cons
- Higher unit costs
- Longer lead times
- Limited production capacity
- Inability to respond to high market demand
Experience the Best of High-Volume With the Stratasys H350
Most 3D printers are known for low-production volumes, but the Stratasys H350 is changing the game. It is built for fast, high production volume to help you produce parts faster and accurately every time.
Amplify your part production quickly and effectively. Learn more about the Stratasys H350 printer.